There is a long list of medical procedures; each plays a vital role in diagnosing and treating diseases from the common cold to cancers. But while each of these procedures is important for us in the medical community, the everyday person may not understand what every single practice is, why they’re important, and what to expect should they be a patient undergoing one of these procedures. For example, one of these procedures is a bone marrow biopsy, so let’s investigate.
What is Bone Marrow?
Let’s start with the basics: what is bone marrow? Within most of our large bones is soft tissue which Let’s start with the basics: what is bone marrow? Within most of our large bones is soft tissue that produces many of the body’s blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. There are two types of stem cells found within the bone marrow—myeloid, which creates red blood cells, platelets, and some white blood cells, and lymphoid, which produces a specific type of white blood cell responsible for immunity.
What is a Bone Marrow Biopsy?
A bone marrow biopsy is a procedure to collect and examine bone marrow, showing whether your bone marrow and the stem cells found within are healthy and producing the normal amount of blood cells. A doctor will use the procedure to diagnose and monitor blood and marrow diseases, including some cancers and any fevers of unknown origin.
So, why are bone marrow biopsies done? The exam will offer detailed information about the condition of both the bone itself and the blood cells within. Your doctor may order a bone marrow exam if blood tests are abnormal or don’t provide enough information about a suspected problem. Specifically, a bone marrow biopsy may be performed to:
- Diagnose a disease or condition involving the bone marrow or blood cells
- Determine the stage or progression of a disease
- Examine iron levels and whether they are adequate
- Monitor treatment of a disease
- Investigate fevers of unknown origin.
What conditions can bone marrow biopsies identify? The procedure is a versatile one since it can identify many issues, including:
- Anemia
- Blood cell conditions in which too few or too many of certain types of blood cells are produced, such as leukopenia, leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis, pancytopenia, and polycythemia
- Cancers of the blood or bone marrow, including leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma
- Cancers that have spread from one area into the bone marrow
- Hemochromatosis
- Fever
What Happens During a Bone Marrow Biopsy?
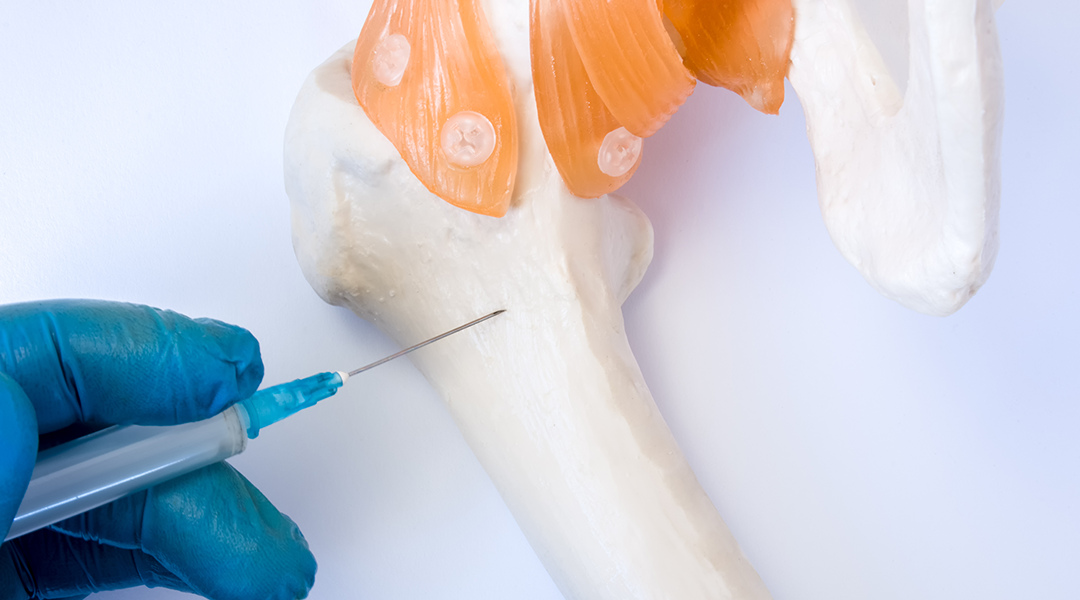
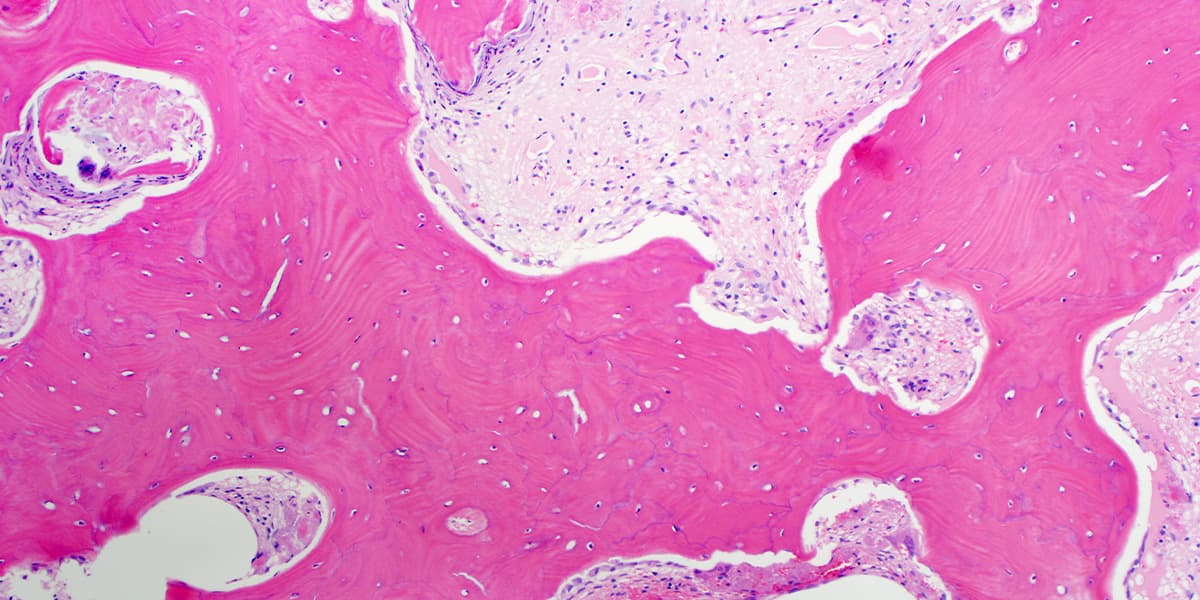
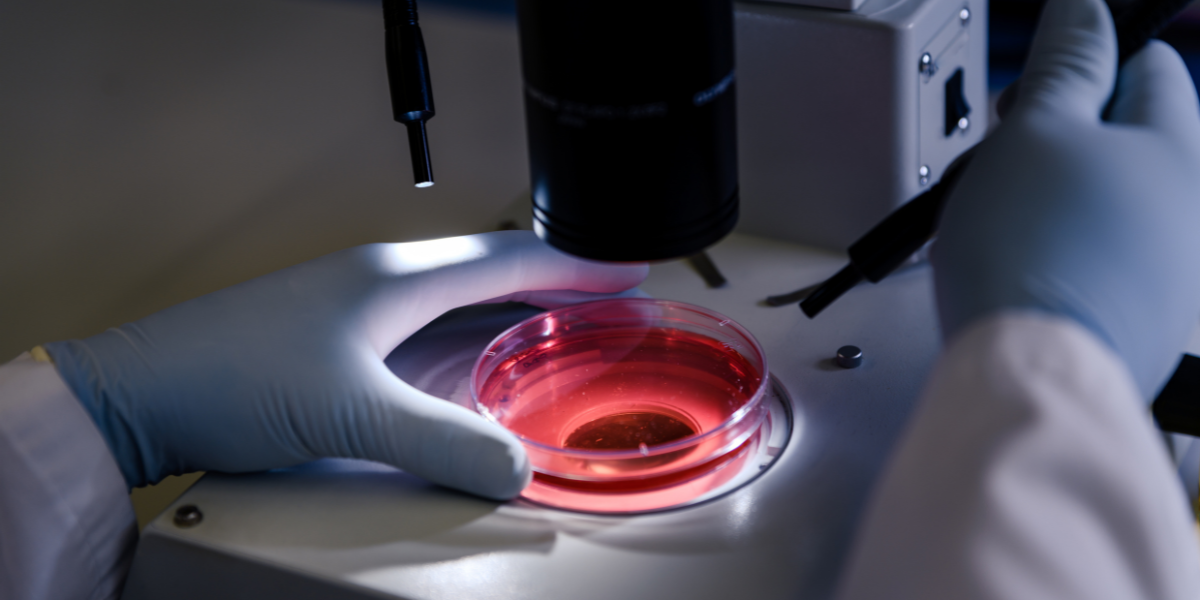
During a bone marrow biopsy, a small sample of the bone and bone marrow within is removed—usually a small sample of the bone and bone marrow within is removed during a bone marrow biopsy—usually from a stem cell-rich area like the pelvis. First, a small area of skin and the surface of the bone underneath are numbed with a local anesthetic. Then a special needle is pushed into the bone and rotated to remove a small sample of bone and the marrow inside. Finally, the sample is sent to a laboratory like the South Bend Medical Foundation so pathologists can look for signs of diseases and help doctors make accurate diagnoses.
A bone marrow biopsy is a quick yet highly accurate procedure that doctors can use to examine bone marrow samples, which can help them diagnose a range of blood diseases and even cancers. It is not a pain-free procedure, but the pain is manageable with a doctor’s help. The South Bend Medical Foundation has a team of experienced pathologists who have devoted years to studying samples, including bone marrow. So, next time you need to have a biopsy done, ask your doctor to send your sample to South Bend Medical Foundation—we’re here for you!